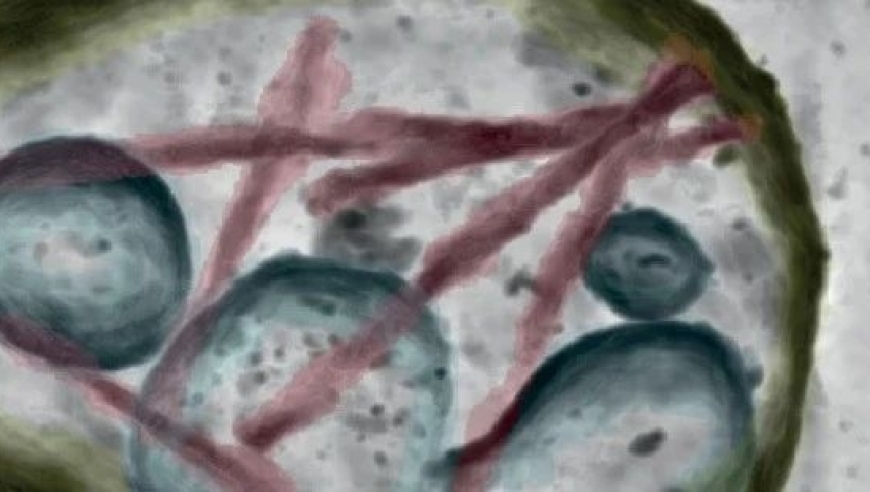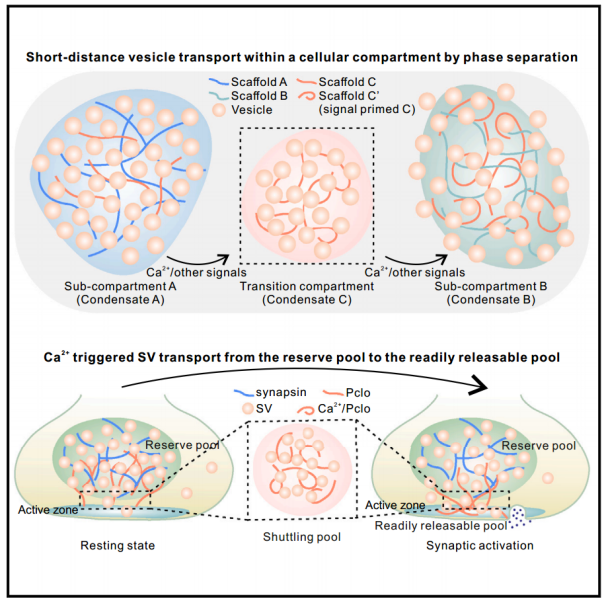
2024年3月,南方科技大学张明杰团队在《Cell》在线发表了“短距离vesicle transport via phase separation”研究成果,通过研究发现,一个大线圈支架蛋白Piccolo通过C2A结构域介导的Ca 2+ 感应可驱动突触蛋白与囊泡的相分离,从而促进突触前亚室之间受调控的定向囊泡运输。同时,Trk融合基因TFG通过相分离参与COPII囊泡从内质网转运到内质网-高尔基体中间区,说明细胞内短距离定向囊泡运输具有普遍性。与远距离分子马达相比,细胞囊泡体积较大、重量沉重,在拥挤的细胞环境中难以有效扩散,故存在一种或多种机制来促进局部细胞室中短途囊泡的快速运动,如基于细胞骨架的分子马达。
短距离vesicle transport via phase separation through C2A protein-driven short-range vesicle movement and the importance of cell-based molecular motors in the cell's compartmentalization
In March 2024, a groundbreaking research paper published by the Southern University of Science and Technology (SUSTech) in the journal Cell, provided insights into an exciting new mechanism for short-distance vesicle transport within neurons: piccolo proteins, mediated by a C2A domain, facilitate the direct recruitment of synaptic proteins to the intracellular interface between the presynaptic and postsynaptic compartments.
The study, led by Professor Zhang Mingjie, a renowned neuroscientist at SUSTech, reported on the discovery that a large-scale network of proteins called piccolo proteins, such as Piccolo, plays a critical role in regulating the selective vesicle trafficking across the synaptic cleft. The C2A domain, located within the piccolo protein, is responsible for coordinating Ca 2+ influx and activation, which in turn triggers the conversion of a novel channel protein named Trk融合 gene, known as TFG, into a potent actin-binding domain (ABD).
C2A proteins interact with the trkA ABD, forming a complex structure that drives the intracellular Ca 2+ gradient towards the presynaptic neuron. This Ca 2+ trigger directly binds to the inner surface of the presynaptic synaptic vesicles, promoting their fusion with the extracellular plasma membrane through a process called exocytosis. When these vesicles reach the synaptic cleft, they serve as the starting point for the short-distance vesicle movement towards the postsynaptic neuron.
Once inside the synaptic cleft, the piccolo proteins target the TrkA ABD to form an efflux-type GTPase-dependent motor protein. This GTPase-dependent motor protein is characterized by a flexible helix that can open and close due to its interactions with various regulators, including cytoskeleton components like microtubules and focal adhesion complexes. The motor protein interacts with the actin cytoskeleton, leading to the conformational changes necessary for the efficient release of tagged TrkA from the synapse.
As the tagged TrkA exits the synaptic cleft, it interacts with a specific subunit of the COPII (Covalent Proteins Ii) complex, which facilitates the targeting of tagged TrkA to the intracellular domain of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). COPII is composed of several subunits, including integral transmembrane receptors, hydrophobic membrane proteins, and a cytoplasmic subcomplex. The COPII subcomplex mediates the selective export of tagged TrkA from the ER, allowing it to bypass the recycling pathway and access the targeted COPII subdomain.
In this particular case, the signal generated by the Ca 2+ trigger stimulates the interaction of the tagged TrkA with the COPII subcomplex, activating a unique sequence within the COPII subdomain. This activated sequence interacts with a specific signaling receptor on the cytoplasmic side of the COPII subcomplex, which then leads to the generation of a PARG (Positive Amplified Glycine Kinase) phosphatase. PARG is a catalytic phosphatase that dephosphorylates the tagging protein, effectively marking it for degradation and limiting its function.
Upon degradation, the tagging protein undergoes further degradation through proteolytic酶, resulting in the complete removal of the tagged TrkA from the ER. The tagged TrkA continues to function as a regulator of cellular intracellular trafficking, serving as a "molecular motor" responsible for driving short-distance vesicle movement within the presynaptic neuron and the postsynaptic neuron.
The findings of this study highlight the remarkable potential of piccolo proteins and TrkA signaling for controlling the spatial distribution of molecules within the cell and facilitating precise cargo delivery within the synaptic cleft. By understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying this phenomenon, researchers may uncover new therapeutic strategies for treating neurological disorders and improving the efficiency of brain-computer interfaces.
Moreover, the involvement of short-range vesicle transport within neuronal circuits has significant implications for understanding the intricate organization and function of neural circuits in the brain. Short-distance vesicle movement provides crucial links between the synaptic input, interneuron communication, and axonal plasticity, thereby contributing to the overall neural development and plasticity of the nervous system.
In conclusion, the study of piccolo proteins and their regulation of short-range vesicle transport via a C2A-driven mechanism offers a groundbreaking insight into the dynamics of intracellular trafficking within neurons. By unraveling the mechanisms underlying this short-distance vesicle-mediated transport, researchers may gain valuable insights into the principles governing cell function and potentially develop new strategies for targeted drug delivery, disease treatment, and improved cognitive abilities. The study underscores the importance of considering the dynamic nature of cell-cell communication and the interplay between various cellular organelles and signaling pathways, revealing how simple yet powerful molecular machines can mediate essential cellular processes.