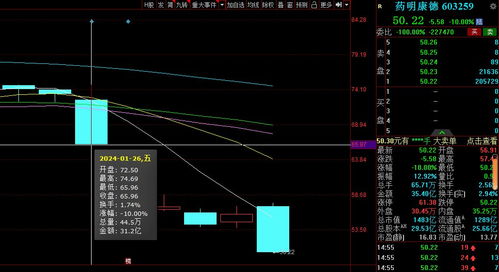
美国共和党议员Mike Gallagher宣布即将从国会辞职,引发各方关注并可能导致法案修订延后对中药制造商产生影响。他提出推行《生物安全法案》,力阻中国快速发展生物技术行业,被批评为法案中最具杀伤力的条款之一,可能削弱对中国生物医药公司的限制措施。法案草案因涉及暂停争议的中国生物技术公司在联邦资助的医疗机构提供服务而遭遇“Held over”延期表决现象,外界猜测美方政府或将在此类中国企业问题上进一步采取行动。这一事件可能会改变未来中美科技合作的走向,特别是在生物科技领域,各国之间的竞争与合作将日益凸显其重要性和紧迫性。

Title: Mike Gallagher's Exit from Congress A Game-Changer for China's Biotechnology Industry

As the 6th Republican Senator from Wisconsin, Mike Gallagher has announced his decision to resign from the US House of Representatives earlier this week. The announcement raised significant interest and sparked debates about potential changes in legislation related to Chinese biotechnology companies. One controversial aspect of the proposed "Biological Safety Act" by Gallagher, which aims to limit American corporations' access to Chinese biological technologies, has received widespread criticism.
The legislation, initially proposed to block Chinese companies with potentially dangerous biosimilars or genetic engineering products from providing medical services in federal healthcare facilities, faces an unexpected challenge due to its broad scope. It encompasses various provisions that threaten the interests of both Chinese pharmaceuticals and American stakeholders, such as requiring foreign biological research institutions to sign binding contracts that restrict their ability to provide services to pharmaceutical companies, effectively inhibiting their commercialization efforts in the United States.
The bill's single most contentious clause, the provision preventing Chinese biotech companies from receiving FDA approvals for biosimilar drugs without prior government funding, has generated intense controversy among health policy experts and trade groups alike. The Committee on Health and Human Services, where the bill is currently being debated, has proposed several amendments that could address some of the concerns raised by the bill's critics, including expanding the definition of biosimilars to include similar products under different regulatory frameworks or introducing a process for granting regulatory approval to foreign pharmaceutical firms.
Despite these efforts, the bill's chances of passage remain uncertain due to a holdover caused by a procedural issue, specifically the "Held Over" designation that prohibits a bill from advancing until it passes through three additional committees. This situation highlights the complexity of managing intergovernmental cooperation and international trade negotiations in the era of growing economic tensions between the US and China, particularly when it comes to matters related to technology.
The uncertainty surrounding the legislation may also have implications for future collaborations between the two nations in the field of biotechnology. As the world continues to grapple with emerging infectious diseases like COVID-19, technological advancements in areas such as vaccine development and personalized medicine are essential for addressing global health challenges. A comprehensive understanding of the limits of Chinese biotechnology capabilities is crucial for fostering healthy competition and ensuring equitable access to innovative treatments.
Moreover, the issue of American biotech companies seeking to establish themselves in China's rapidly growing market has been a matter of concern for policymakers and businesses alike. With China now accounting for a significant portion of the global biotech industry, policies that promote collaboration and innovation at the local level can help facilitate investment and talent exchange, ultimately benefiting both countries' economies.
In conclusion, Mike Gallagher's exit from Congress marks a significant shift in the geopolitical landscape in the United States' relationship with China. The proposed "Biological Safety Act" poses a formidable obstacle to Chinese biotech companies seeking to gain access to the American market, particularly in terms of gaining FDA approvals for biosimilar drugs without prior government funding. However, it is also likely that Congress will continue to explore alternative approaches to addressing these concerns, which may involve revising existing regulations or introducing new mechanisms to promote healthy competition and innovation in the biotech sector.
The unforeseen consequences of the "Held Over" holdover on the Bill's progression raise important questions about how the US Senate balances its commitment to free trade and intellectual property rights with the need to protect public health and ensure fair access to scientific discoveries. In the face of ongoing geopolitical tensions and the rapidly evolving biotechnology landscape, the outcome of the debate on this legislation will be critical for determining the direction of US-China relations in the years to come.